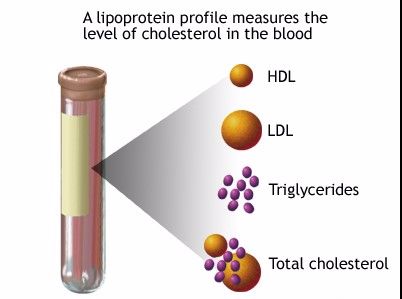
Mission Non-fasting lipid test takes 45 seconds. | The lipid profile is used as part of a cardiac risk assessment to help determine an individual's risk of heart disease and to help make decisions about what treatment may be best if there is borderline or high risk. Thus, it is import that you have a complete blood profile versus just a Total Cholesterol and HDL test, which can hide risk factors. Lipids are a group of fats and fat-like substances that are important constituents of cells and sources of energy. Monitoring and maintaining healthy levels of these lipids is important in staying healthy. The results of the lipid profile are considered along with other known risk factors of heart disease to develop a plan of treatment and follow-up. Depending on the results and other risk factors, treatment options may involve lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise or lipid-lowering medications such as statins. A lipid profile includes: Total cholesterol — this test measures all of the cholesterol in all the lipoprotein particles. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) — measures the cholesterol in HDL particles; often called "good cholesterol" because it removes excess cholesterol and carries it to the liver for removal. |

Why Lipid Profile Test?
Established in 1982
Fitech UK Ltd is registered in England Reg 5532915
7 Viceroy House
Southampton
SO15 1HY
United Kingdom
t. 0118 3240 061